Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone-Secreting Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumor (TSH PitNET): A Single-Center Experience
- Jung Heo, Yeon-Lim Suh, Se Hoon Kim, Doo-Sik Kong, Do-Hyun Nam, Won-Jae Lee, Sung Tae Kim, Sang Duk Hong, Sujin Ryu, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):387-396. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1877
- 851 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
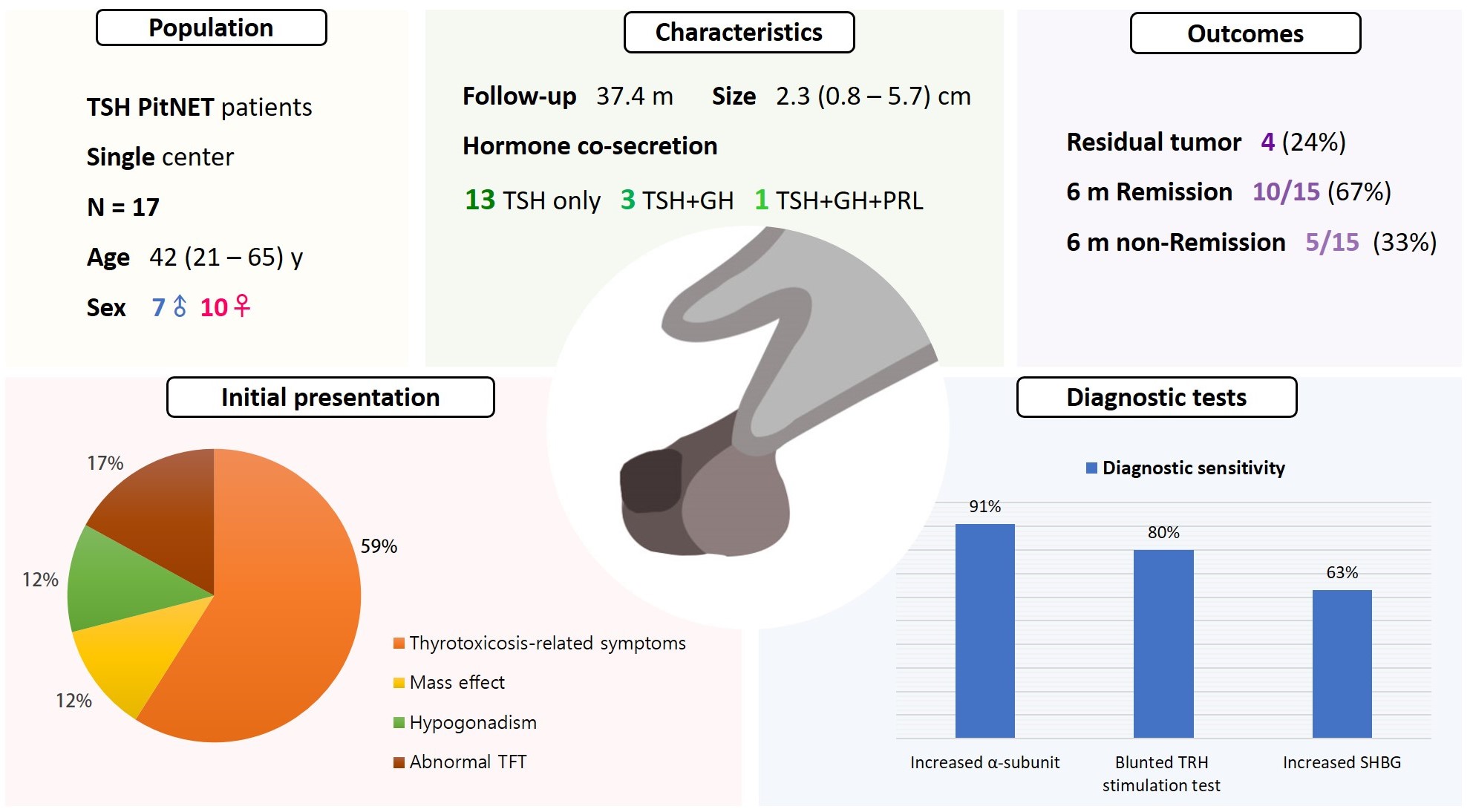
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-secreting pituitary neuroendocrine tumor (TSH PitNET) is a rare subtype of PitNET. We investigated the comprehensive characteristics and outcomes of TSH PitNET cases from a single medical center. Also, we compared diagnostic methods to determine which showed superior sensitivity.
Methods
A total of 17 patients diagnosed with TSH PitNET after surgery between 2002 and 2022 in Samsung Medical Center was retrospectively reviewed. Data on comprehensive characteristics and treatment outcomes were collected. The sensitivities of diagnostic methods were compared.
Results
Seven were male (41%), and the median age at diagnosis was 42 years (range, 21 to 65); the median follow-up duration was 37.4 months. The most common (59%) initial presentation was hyperthyroidism-related symptoms. Hormonal co-secretion was present in four (23%) patients. Elevated serum alpha-subunit (α-SU) showed the greatest diagnostic sensitivity (91%), followed by blunted response at thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulation (80%) and elevated sex hormone binding globulin (63%). Fourteen (82%) patients had macroadenoma, and a specimen of one patient with heavy calcification was negative for TSH. Among 15 patients who were followed up for more than 6 months, 10 (67%) achieved hormonal and structural remission within 6 months postoperatively. A case of growth hormone (GH)/TSH/prolactin (PRL) co-secreting mixed gangliocytoma-pituitary adenoma (MGPA) was discovered.
Conclusion
The majority of the TSH PitNET cases was macroadenoma, and 23% showed hormone co-secretion. A rare case of GH/TSH/PRL co-secreting MGPA was discovered. Serum α-SU and TRH stimulation tests showed great diagnostic sensitivity. Careful consideration is needed in diagnosing TSH PitNET. Achieving remission requires complete tumor resection. In case of nonremission, radiotherapy or medical therapy can improve the long-term remission rate.

- Adrenal Gland
- Urinary Free Metanephrines for Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma
- Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Yun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Youn Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):697-701. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.925
- 4,397 View
- 188 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
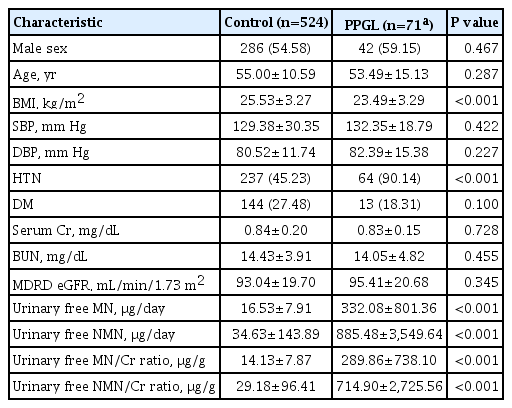
Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL) is diagnosed through biochemical confirmation of excessive catecholamines in urine and plasma. Recent technological developments have allowed us to measure urinary free metanephrines; however, the diagnostic accuracy of these new methods and the diagnostic cutoff values have not been evaluated.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of 595 subjects, including 71 PPGL cases and 524 controls. PPGL was based on pathological confirmation. Subjects with no evidence of PPGL over 2 years were included in the control group.
Results
Urinary free metanephrines yielded similar area under the curve (AUC) to urinary fractionated metanephrines and plasma free metanephrines. However, urinary free normetanephrine yielded a better AUC than did urinary fractionated normetanephrine. The optimal cutoff for urinary free metanephrine and normetanephrine corrected for urinary creatinine yielded 97.2% sensitivity and 98.1% specificity.
Conclusion
Urinary free metanephrines are a reliable method for diagnosing PPGL in Asian populations compared with existing biochemical methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biochemical Assessment of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma
Graeme Eisenhofer, Christina Pamporaki, Jacques W M Lenders
Endocrine Reviews.2023; 44(5): 862. CrossRef - Adrenal bleeding due to pheochromocytoma - A call for algorithm
Ewelina Rzepka, Joanna Kokoszka, Anna Grochowska, Magdalena Ulatowska-Białas, Martyna Lech, Marta Opalińska, Elwira Przybylik-Mazurek, Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Alicja Hubalewska-Dydejczyk
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Biochemical Assessment of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma

- Miscellaneous
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,491 View
- 428 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
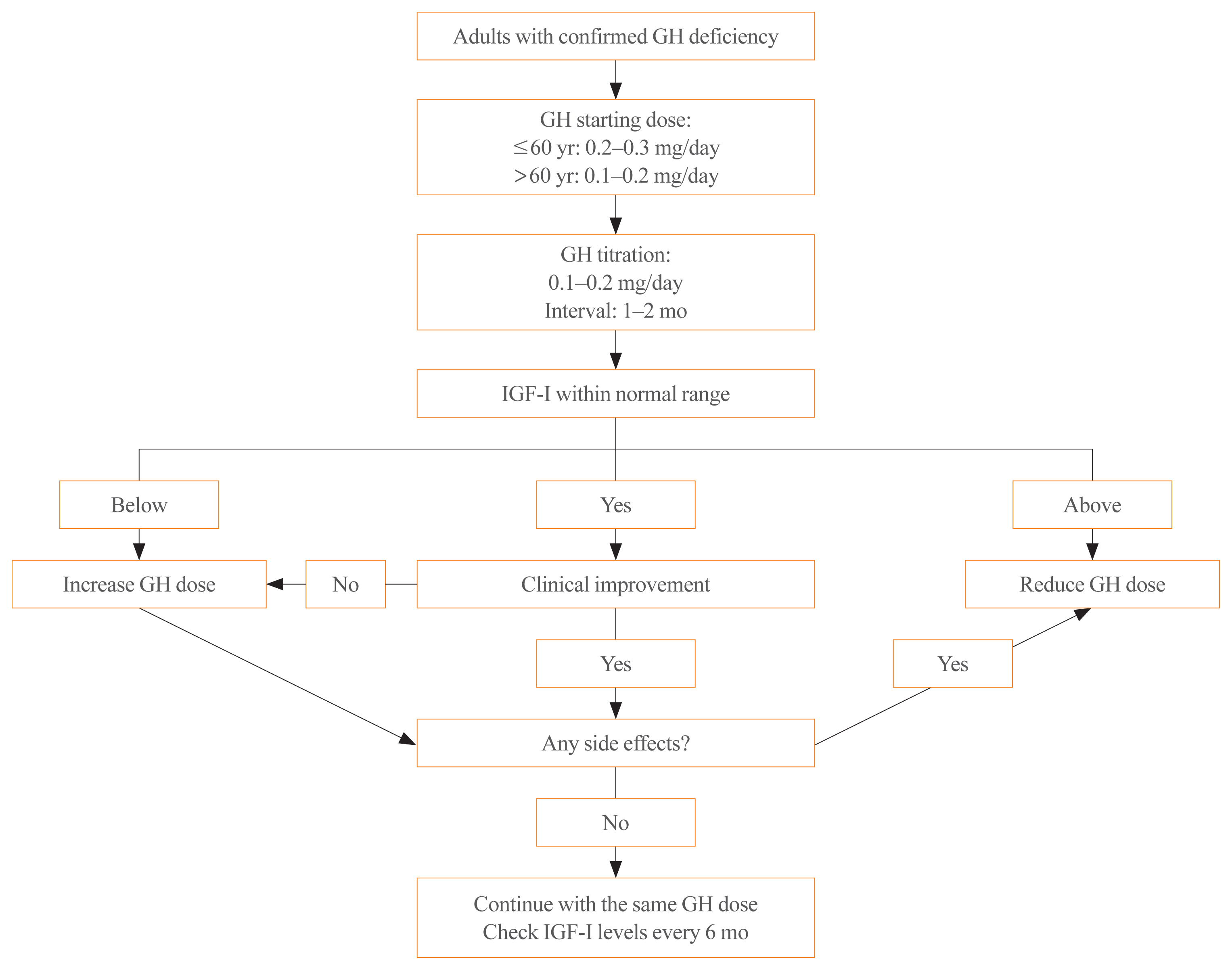
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Impact of Skeletal Muscle Mass on Metabolic Health
- Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):1-6. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.1
- 10,689 View
- 293 Download
- 64 Web of Science
- 68 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Skeletal muscle is regarded as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Muscle-derived secretory proteins, referred to as myokines, mediate interactions between skeletal muscle mass and other organs such as the liver, adipose tissue, pancreas, bone, and the cardiovascular system. As individuals age, reduced levels of physical activity and sarcopenia (loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength) are associated with physical frailty and disability. Recently, several studies have suggested that the loss of skeletal muscle mass may contribute to metabolic disease. Therefore, herein, we focus on the relationships between skeletal muscle mass and metabolic diseases, including metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex differences in the association between dual‐energy x‐ray absorptiometry‐measured body composition and periodontitis
Peijun Zhu, An Li, Qingqing Cai, Yuntao Chen, Yang Liu, Harriët Jager‐Wittenaar, Geerten‐Has E. Tjakkes, Shulan Xu
Journal of Periodontology.2024; 95(3): 219. CrossRef - Advances in the treatment of functional male hypogonadism
Giovanni Corona, Giulia Rastrelli, Clotilde Sparano, Linda Vignozzi, Alessandra Sforza, Mario Maggi
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(2): 163. CrossRef - Heterogeneously elevated branched-chain/aromatic amino acids among new-onset type-2 diabetes mellitus patients are potentially skewed diabetes predictors
Min Wang, Yang Ou, Xiang-Lian Yuan, Xiu-Fang Zhu, Ben Niu, Zhuang Kang, Bing Zhang, Anwar Ahmed, Guo-Qiang Xing, Heng Su
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(1): 53. CrossRef - The Vicious Cycle of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Skeletal Muscle Atrophy: Clinical, Biochemical, and Nutritional Bases
Jose M. Lopez-Pedrosa, Maria Camprubi-Robles, German Guzman-Rolo, Andres Lopez-Gonzalez, Jose Manuel Garcia-Almeida, Alejandro Sanz-Paris, Ricardo Rueda
Nutrients.2024; 16(1): 172. CrossRef - FGF21 Induces Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Increases Amino Acids in Female Mice: A Potential Role for Glucocorticoids
Karlton R Larson, Devi Jayakrishnan, Karla A Soto Sauza, Michael L Goodson, Aki T Chaffin, Arik Davidyan, Suraj Pathak, Yanbin Fang, Diego Gonzalez Magaña, Benjamin F Miller, Karen K Ryan
Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality risk relationship using standard categorized BMI or knee-height based BMI – does the overweight/lower mortality paradox hold true?
Nivetha Natarajan Gavriilidou, Mats Pihlsgård, Sölve Elmståhl, Henrik Ekström
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gromwell (Lithospermum erythrorhizon) Attenuates High-Fat-Induced Skeletal Muscle Wasting by Increasing Protein Synthesis and Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Ji-Sun Kim, Hyunjung Lee, Ahyoung Yoo, Hang Yeon Jeong, Chang Hwa Jung, Jiyun Ahn, Tae-Youl Ha
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2024; 34(3): 495. CrossRef - L-shaped association between lean body mass to visceral fat mass ratio with hyperuricemia: a cross-sectional study
Longti Li, Ya Shao, Huiqin Zhong, Yu Wang, Rong Zhang, Boxiong Gong, Xiaoxv Yin
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of adiposity-based chronic disease and its association with anthropometric and clinical indices: a cross-sectional study
Luis E González-Salazar, Aurora E Serralde-Zúñiga, Adriana Flores-López, Juan P Díaz-Sánchez, Isabel Medina-Vera, Edgar Pichardo-Ontiveros, Rocío Guizar-Heredia, Karla G Hernández-Gómez, Ana Vigil-Martínez, Liliana Arteaga-Sánchez, Azalia Avila-Nava, Nata
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 130(1): 93. CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle Myokine Expression in Critical Illness, Association With Outcome and Impact of Therapeutic Interventions
Ilse Vanhorebeek, Jan Gunst, Michaël P Casaer, Inge Derese, Sarah Derde, Lies Pauwels, Johan Segers, Greet Hermans, Rik Gosselink, Greet Van den Berghe
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Circadian Rhythm Disturbance on the Human Musculoskeletal System and the Importance of Nutritional Strategies
Norsham Juliana, Liyana Azmi, Nadia Mohd Effendy, Nur Islami Mohd Fahmi Teng, Izuddin Fahmy Abu, Nur Nabilah Abu Bakar, Sahar Azmani, Noor Anisah Abu Yazit, Suhaini Kadiman, Srijit Das
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 734. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of post‐burn muscle wasting and the therapeutic potential of physical exercise
Dorien Dombrecht, Ulrike Van Daele, Birgit Van Asbroeck, David Schieffelers, Pieter‐Jan Guns, Nick Gebruers, Jill Meirte, Eric van Breda
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(2): 758. CrossRef - Metabolic Impact of Frailty Changes Diabetes Trajectory
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Metabolites.2023; 13(2): 295. CrossRef - From Single- to Multi-organ-on-a-Chip System for Studying Metabolic Diseases
Minjeong Jang, Hong Nam Kim
BioChip Journal.2023; 17(2): 133. CrossRef - INFLUENCE OF SARCOPENIA ON THE COURSE AND PROGNOSIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEART FAILURE
Gulyaev N.I., Adamov A.A., Akhmetshin I.M.
"Medical & pharmaceutical journal "Pulse".2023; : 124. CrossRef - Frailty and the Interactions between Skeletal Muscle, Bone, and Adipose Tissue-Impact on Cardiovascular Disease and Possible Therapeutic Measures
María Elena Soto, Israel Pérez-Torres, María Esther Rubio-Ruiz, Agustina Cano-Martínez, Linaloe Manzano-Pech, Verónica Guarner-Lans
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4534. CrossRef - Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Buffer Proteins: A Focus on the Yet-To-Be-Explored Role of Sarcalumenin in Skeletal Muscle Health and Disease
Elena Conte, Giorgia Dinoi, Paola Imbrici, Annamaria De Luca, Antonella Liantonio
Cells.2023; 12(5): 715. CrossRef - Antarctic krill extracts enhance muscle regeneration and muscle function via mammalian target of rapamycin regulation
Seongmin Lee, Mi-Ock Baek, Sana Abdul Khaliq, Amna Parveen, Sun Yeou Kim, Jin-Hyoung Kim, Il-Chan Kim, Mee-Sup Yoon
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 103: 105483. CrossRef - Pharmacological and physiological roles of adipokines and myokines in metabolic-related dementia
Archana Arjunan, Juhyun Song
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 163: 114847. CrossRef - PRMT5 links lipid metabolism to contractile function of skeletal muscles
Kun Ho Kim, Zhihao Jia, Madigan Snyder, Jingjuan Chen, Jiamin Qiu, Stephanie N Oprescu, Xiyue Chen, Sabriya A Syed, Feng Yue, Bruno T Roseguini, Anthony N Imbalzano, Changdeng Hu, Shihuan Kuang
EMBO reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Biqi” Bayberry Extract Promotes Skeletal Muscle Fiber Type Remodeling by Increasing Fast Myofiber Formation via the Akt/FoxO1 Pathway in Mice
Jinjie Li, Yi Li, Xiangying Suo, Jiangtao Li, Da Huang, Guangning Kou
Foods.2023; 12(13): 2471. CrossRef - Effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on skeletal muscle atrophy, function, and myokine profile in diabetic myopathy
Yeşim Özçatal, Fırat Akat, Yakup Tatar, Hakan Fıçıcılar, Bilge Serdaroğlu, Ferda Topal Çelikkan, Metin Baştuğ
Cytokine.2023; 169: 156279. CrossRef - Impaired proteostatic mechanisms other than decreased protein synthesis limit old skeletal muscle recovery after disuse atrophy
Jordan D. Fuqua, Marcus M. Lawrence, Zachary R. Hettinger, Agnieszka K. Borowik, Parker L. Brecheen, Marcelina M. Szczygiel, Claire B. Abbott, Frederick F. Peelor, Amy L. Confides, Michael Kinter, Sue C. Bodine, Esther E. Dupont‐Versteegden, Benjamin F. M
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(5): 2076. CrossRef - Body physique rating as a factor to identify at-risk Mexicans for Metabolic Syndrome
Oscar Herrera-Fomperosa, Sergio K. Bustamante-Villagomez, Sarahí Vazquez-Álvarez, Gabriela Vázquez-Marroquín, Leonardo M. Porchia, Enrique Torres-Rasgado, Ricardo Pérez-Fuentes, M. Elba Gonzalez-Mejia
Human Nutrition & Metabolism.2023; 33: 200206. CrossRef - Association between Fractional Oxygen Extraction from Resting Quadriceps Muscle and Body Composition in Healthy Men
Rodrigo Yáñez-Sepúlveda, Jorge Olivares-Arancibia, Guillermo Cortés-Roco, Aldo Vasquez-Bonilla, Matías Monsalves-Álvarez, Ildefonso Alvear-Órdenes, Marcelo Tuesta
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2023; 8(4): 149. CrossRef - Correlations between Mental Health, Physical Activity, and Body Composition in American College Students after the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown
Luis Torres, Manuela C. Caciula, Alin S. Tomoiaga, Carmen Gugu-Gramatopol
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(22): 7045. CrossRef - Association between total body muscle percentage and prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults findings from an 18-year follow-up: a prospective cohort study
Byoung Chan Ahn, Chul Yong Park, Jung Hee Hong, Ki Ook Baek
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(Suppl): S47. CrossRef - The independent and joint associations among muscle strength, abdominal obesity and cardiometabolic variables among adults
Tiago Rodrigues de Lima, David Alejandro González‐Chica, Xuemei Sui, Diego Augusto Santos Silva
European Journal of Sport Science.2022; 22(7): 1122. CrossRef - Mentale Gesundheit und physische Aktivität
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2022; 60(1): 13. CrossRef - A new paradigm in sarcopenia: Cognitive impairment caused by imbalanced myokine secretion and vascular dysfunction
Danbi Jo, Gwangho Yoon, Oh Yoen Kim, Juhyun Song
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 147: 112636. CrossRef - Sarcopenia Is a Cause and Consequence of Metabolic Dysregulation in Aging Humans: Effects of Gut Dysbiosis, Glucose Dysregulation, Diet and Lifestyle
James W. Daily, Sunmin Park
Cells.2022; 11(3): 338. CrossRef - Leveraging deep phenotyping from health check-up cohort with 10,000 Korean individuals for phenome-wide association study of 136 traits
Eun Kyung Choe, Manu Shivakumar, Anurag Verma, Shefali Setia Verma, Seung Ho Choi, Joo Sung Kim, Dokyoon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Zika virus disrupts gene expression in human myoblasts and myotubes: Relationship with susceptibility to infection
Ingo Riederer, Daniella Arêas Mendes-da-Cruz, Guilherme Cordenonsi da Fonseca, Mariela Natacha González, Otavio Brustolini, Cássia Rocha, Guilherme Loss, Joseane Biso de Carvalho, Mariane Talon Menezes, Lidiane Menezes Souza Raphael, Alexandra Gerber, Myr
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2022; 16(2): e0010166. CrossRef - Teil 1: Muskeldysfunktionen – mit Training gegen Schmerz
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2022; 60(2): 84. CrossRef - Transcription factors KLF15 and PPARδ cooperatively orchestrate genome-wide regulation of lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle
Liyan Fan, David R. Sweet, Erica K. Fan, Domenick A. Prosdocimo, Annmarie Madera, Zhen Jiang, Roshan Padmanabhan, Saptarsi M. Haldar, Vinesh Vinayachandran, Mukesh K. Jain
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2022; 298(6): 101926. CrossRef - An Overview of the TRP-Oxidative Stress Axis in Metabolic Syndrome: Insights for Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Mizael C. Araújo, Suzany H. S. Soczek, Jaqueline P. Pontes, Leonardo A. C. Marques, Gabriela S. Santos, Gisele Simão, Laryssa R. Bueno, Daniele Maria-Ferreira, Marcelo N. Muscará, Elizabeth S. Fernandes
Cells.2022; 11(8): 1292. CrossRef - Effects of a 10-Week Physical Activity Intervention on Asylum Seekers’ Physiological Health
Matheus Guerra, Danilo Garcia, Maryam Kazemitabar, Erik Lindskär, Erica Schütz, Daniel Berglind
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(7): 822. CrossRef - Low muscle mass and mortality risk later in life: A 10-year follow-up study
Cristina Camargo Pereira, Valéria Pagotto, Cesar de Oliveira, Erika Aparecida Silveira, Kiyoshi Sanada
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(7): e0271579. CrossRef - Independent and joint associations of weightlifting and aerobic activity with all-cause, cardiovascular disease and cancer mortality in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial
Jessica Gorzelitz, Britton Trabert, Hormuzd A Katki, Steven C Moore, Eleanor L Watts, Charles E Matthews
British Journal of Sports Medicine.2022; 56(22): 1277. CrossRef - Handgrip Strength Cutoff Value Among Korean Adolescents with Metabolic Syndrome Components: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data 2014–2017
Chang Hoon Lee, Jun Hyeok Lee, Yong Whi Jeong, Hong Koh, Yunkoo Kang
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 584. CrossRef - Physical activity level, sitting time, and skeletal muscle mass between esports players and non-esports players
Zhi H. SEE, Mohamad S. ABDUL HAMID
Gazzetta Medica Italiana Archivio per le Scienze Mediche.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of the Nutrition–Inflammation Status on the Functionality of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Ángel Nogueira, Graciela Álvarez, Guillermina Barril
Nutrients.2022; 14(22): 4745. CrossRef - Does Timing Matter? A Narrative Review of Intermittent Fasting Variants and Their Effects on Bodyweight and Body Composition
Alan A. Aragon, Brad J. Schoenfeld
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 5022. CrossRef - Sex- and region-specific associations of skeletal muscle mass with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Pei Xiao, Pu Liang, Panjun Gao, Jinyi Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Donor Skeletal Muscle Quality Affects Graft Mortality After Living Donor Liver Transplantation- A Single Center, Retrospective Study
Takahiro Tomiyama, Noboru Harada, Takeo Toshima, Yuki Nakayama, Katsuya Toshida, Akinari Morinaga, Yukiko Kosai-Fujimoto, Takahiro Tomino, Takeshi Kurihara, Kazuki Takeishi, Yoshihiro Nagao, Kazutoyo Morita, Shinji Itoh, Tomoharu Yoshizumi
Transplant International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Handgrip Strength Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents: Analysis of Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2014–2018
Hae Woon Jung, Jieun Lee, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 334. CrossRef - Diet quality and a traditional dietary pattern predict lean mass in Australian women: Longitudinal data from the Geelong Osteoporosis Study
Jessica A. Davis, Mohammadreza Mohebbi, Fiona Collier, Amy Loughman, Nitin Shivappa, James R. Hébert, Julie A. Pasco, Felice N. Jacka
Preventive Medicine Reports.2021; 21: 101316. CrossRef - Association between serum FGF21 level and sarcopenia in older adults
Hee-Won Jung, Jin Hoon Park, Da Ae Kim, Il-Young Jang, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Seungjoo Lee, Jeoung Hee Kim, Hyon-Seung Yi, Eunju Lee, Beom-Jun Kim
Bone.2021; 145: 115877. CrossRef - Benchside to the bedside of frailty and cardiovascular aging: Main shared cellular and molecular mechanisms
Sandra Maria Barbalho, Ricardo José Tofano, Eduardo Federigui Baisi Chagas, Cláudia Rucco Penteado Detregiachi, Ricardo de Alvares Goulart, Uri Arian Princ Flato
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 148: 111302. CrossRef - Effect of CCL11 on In Vitro Myogenesis and Its Clinical Relevance for Sarcopenia in Older Adults
Da Ae Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Jeoung Hee Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Eunju Lee, Il-Young Jang, Hee-Won Jung, Jin Hoon Park, Beom-Jun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 455. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity as a determinant of cardiovascular disease risk in older people: a systematic review
Katherine Evans, Dima Abdelhafiz, Ahmed H Abdelhafiz
Postgraduate Medicine.2021; 133(8): 831. CrossRef - Decreased continuous sitting time increases heart rate variability in patients with cardiovascular risk factors
Natsuki Nakayama, Masahiko Miyachi, Koji Tamakoshi, Toshio Hayashi, Koji Negi, Koji Watanabe, Makoto Hirai, Sharon Mary Brownie
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0253399. CrossRef - Muskeltraining – ein universelles Medikament
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2021; 59(3): 179. CrossRef - The Effects of Oxytocin on Appetite Regulation, Food Intake and Metabolism in Humans
Liya Kerem, Elizabeth A. Lawson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(14): 7737. CrossRef - Weight Loss Strategies and the Risk of Skeletal Muscle Mass Loss
David McCarthy, Aloys Berg
Nutrients.2021; 13(7): 2473. CrossRef - Association of FGF‐19 and FGF‐21 levels with primary sarcopenia
Rabia Bag Soytas, Veysel Suzan, Pinar Arman, Tugce Emiroglu Gedik, Damla Unal, Mahir Cengiz, Ibrahim Murat Bolayirli, Deniz Suna Erdincler, Alper Doventas, Hakan Yavuzer
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2021; 21(10): 959. CrossRef - Der Muskulatur mehr Aufmerksamkeit schenken!
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2021; 59(4): 302. CrossRef - Methodology, clinical applications, and future directions of body composition analysis using computed tomography (CT) images: A review
Antti Tolonen, Tomppa Pakarinen, Antti Sassi, Jere Kyttä, William Cancino, Irina Rinta-Kiikka, Said Pertuz, Otso Arponen
European Journal of Radiology.2021; 145: 109943. CrossRef - Waist and hip circumference are independently associated with the risk of liver disease in population‐based studies
Oscar Danielsson, Markku J. Nissinen, Antti Jula, Veikko Salomaa, Satu Männistö, Annamari Lundqvist, Markus Perola, Fredrik Åberg
Liver International.2021; 41(12): 2903. CrossRef - Understanding of sarcopenia: from definition to therapeutic strategies
Jee Won Kim, Ryuni Kim, Hyerim Choi, Sang-Jin Lee, Gyu-Un Bae
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2021; 44(9-10): 876. CrossRef - Muscle strength and its association with cardiometabolic variables in adolescents: does the expression of muscle strength values matter?
Tiago Rodrigues de Lima, Xuemei Sui, Luiz Rodrigo Augustemak de Lima, Diego Augusto Santos Silva
World Journal of Pediatrics.2021; 17(6): 597. CrossRef - Musclin Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Body Composition, but Not to Body Mass Index or Cardiorespiratory Capacity in Adults
Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis Valbuena, Andrés F. Milán, María C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Miguel Peña, Mauricio Estrada-Castrillón, Juan C. Aristizábal, Raúl Narvez-Sanchez, Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1055. CrossRef - Physical Exercise and Myokines: Relationships with Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Complications
Sandra Maria Barbalho, Uri Adrian Prync Flato, Ricardo José Tofano, Ricardo de Alvares Goulart, Elen Landgraf Guiguer, Cláudia Rucco P. Detregiachi, Daniela Vieira Buchaim, Adriano Cressoni Araújo, Rogério Leone Buchaim, Fábio Tadeu Rodrigues Reina, Piero
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(10): 3607. CrossRef Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Association with Grip Strength in Older Adults: Findings from the HOPE Study
Reshma Aziz Merchant, Yiong Huak Chan, Jia Yi Lim, John E Morley
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2677. CrossRef- Lower Serum n-3 Fatty Acid Level in Older Adults with Sarcopenia
Il-Young Jang, Hee-Won Jung, Jin Hoon Park, Jeoung Hee Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Eunju Lee, Jin Young Lee, So Jeong Park, Da Ae Kim, Su Jung Kim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Beom-Jun Kim
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 2959. CrossRef - Advances in understanding of health‐promoting benefits of medicine and food homology using analysis of gut microbiota and metabolomics
Minmin Yang, Tao Yan, Meng Yu, Jie Kang, Ruoxi Gao, Peng Wang, Yuhuan Zhang, Huafeng Zhang, Lin Shi
Food Frontiers.2020; 1(4): 398. CrossRef - The association of circulating kynurenine, a tryptophan metabolite, with frailty in older adults
Il-Young Jang, Jin Hoon Park, Jeoung Hee Kim, Seungjoo Lee, Eunju Lee, Jin Young Lee, So Jeong Park, Da Ae Kim, Mark W. Hamrick, Beom-Jun Kim
Aging.2020; 12(21): 22253. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and Muscle Aging: A Brief Overview
Tam Dao, Alexander E. Green, Yun A Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Ki-Tae Ha, Karim Gariani, Mi-ra Lee, Keir J. Menzies, Dongryeol Ryu
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 716. CrossRef
- Sex differences in the association between dual‐energy x‐ray absorptiometry‐measured body composition and periodontitis

- Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
- Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):274-280. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.274
- 5,248 View
- 175 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the beneficial effects of statin treatment in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis have been well studied, there is limited information regarding the renal effects of statins in diabetic nephropathy. We aimed to investigate whether, and which, statins affected renal function in Asian patients with diabetes.
Methods We enrolled 484 patients with diabetes who received statin treatment for more than 12 months. We included patients treated with moderate-intensity dose statin treatment (atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg/day or rosuvastatin 5 to 10 mg/day). The primary outcome was a change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during the 12-month statin treatment, and rapid renal decline was defined as a >3% reduction in eGFR in a 1-year period.
Results In both statin treatment groups, patients showed improved serum lipid levels and significantly reduced eGFRs (from 80.3 to 78.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 for atorvastatin [
P =0.012], from 79.1 to 76.1 mL/min/1.73 m2 for rosuvastatin [P =0.001]). A more rapid eGFR decline was observed in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group (48.7% vs. 38.6%,P =0.029). Multiple logistic regression analyses demonstrated more rapid renal function loss in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group after adjustment for other confounding factors (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 2.42).Conclusion These results suggest that a moderate-intensity dose of atorvastatin has fewer detrimental effects on renal function than that of rosuvastatin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial
Chan Joo Lee, Woong Chol Kang, Sang Hyun Ihm, Il Suk Sohn, Jong Shin Woo, Jin Won Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Jung Hyun Choi, Jung‐Won Suh, Jae‐Bin Seo, Joon‐Hyung Doh, Jung‐Woo Son, Jae‐Hyeong Park, Ju‐Hee Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jung Ho Heo, Jinho Shin, Seok‐Min
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(3): 262. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Guggulutiktaka ghrita on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Samreen M. Sheik, Pugazhandhi Bakthavatchalam, Revathi P. Shenoy, Basavaraj S. Hadapad, Deepak Nayak M, Monalisa Biswas, Varashree Bolar Suryakanth
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2022; 13(3): 100583. CrossRef - The challenge of reducing residual cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease
Stefan Mark Nidorf
European Heart Journal.2022; 43(46): 4845. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improving Prevention and Treatment Options
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Drugs & Aging.2020; 37(8): 567. CrossRef - Intracellular Mechanism of Rosuvastatin-Induced Decrease in Mature hERG Protein Expression on Membrane
Pan-Feng Feng, Bo Zhang, Lei Zhao, Qing Fang, Yan Liu, Jun-Nan Wang, Xue-Qi Xu, Hui Xue, Yang Li, Cai-Chuan Yan, Xin Zhao, Bao-Xin Li
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2019; 16(4): 1477. CrossRef - The problem of safety of lipid-lowering therapy
M V. Zykov
Kardiologiia.2019; 59(5S): 13. CrossRef - Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction
Titus WL Lau, Kevin E.K. Tan, Jason C.J. Choo, Tsun‐Gun Ng, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Juliana C.N. Chan
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(3): 200. CrossRef - Lipids: a personal view of the past decade
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P Mikhailidis
Hormones.2018; 17(4): 461. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial

- Bone Metabolism
- Increased Sclerostin Levels after Further Ablation of Remnant Estrogen by Aromatase Inhibitors
- Wonjin Kim, Yoonjung Chung, Se Hwa Kim, Sehee Park, Jae Hyun Bae, Gyuri Kim, Su Jin Lee, Jo Eun Kim, Byeong-Woo Park, Sung-Kil Lim, Yumie Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):58-64. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.58
- 4,095 View
- 36 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sclerostin is a secreted Wnt inhibitor produced almost exclusively by osteocytes, which inhibits bone formation. Aromatase inhibitors (AIs), which reduce the conversion of steroids to estrogen, are used to treat endocrine-responsive breast cancer. As AIs lower estrogen levels, they increase bone turnover and lower bone mass. We analyzed changes in serum sclerostin levels in Korean women with breast cancer who were treated with an AI.
Methods We included postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer (
n =90; mean age, 57.7 years) treated with an AI, and compared them to healthy premenopausal women (n =36; mean age, 28.0 years). The subjects were randomly assigned to take either 5 mg alendronate with 0.5 µg calcitriol (n =46), or placebo (n =44) for 6 months.Results Postmenopausal women with breast cancer had significantly higher sclerostin levels compared to those in premenopausal women (27.8±13.6 pmol/L vs. 23.1±4.8 pmol/L,
P <0.05). Baseline sclerostin levels positively correlated with either lumbar spine or total hip bone mineral density only in postmenopausal women (r =0.218 andr =0.233;P <0.05, respectively). Serum sclerostin levels increased by 39.9%±10.2% 6 months after AI use in postmenopausal women; however, no difference was observed between the alendronate and placebo groups (39.9%±10.2% vs. 55.9%±9.13%,P >0.05).Conclusion Serum sclerostin levels increased with absolute deficiency of residual estrogens in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer who underwent AI therapy with concurrent bone loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Voluntary Wheel Running Partially Compensates for the Effects of Global Estrogen Receptor-α Knockout on Cortical Bone in Young Male Mice
Rebecca K. Dirkes, Nathan C. Winn, Thomas J. Jurrissen, Dennis B. Lubahn, Victoria J. Vieira-Potter, Jaume Padilla, Pamela S. Hinton
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(4): 1734. CrossRef - Role of Osteocytes in Cancer Progression in the Bone and the Associated Skeletal Disease
Manish Adhikari, Jesús Delgado-Calle
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2021; 19(3): 247. CrossRef - Gestational and lactational exposure to BPA or BPS has minimal effects on skeletal outcomes in adult female mice
Rebecca K. Dirkes, Rebecca J. Welly, Jiude Mao, Jessica Kinkade, Victoria J. Vieira-Potter, Cheryl S. Rosenfeld, Pamela S. Bruzina
Bone Reports.2021; 15: 101136. CrossRef - Modulation of bone turnover aberration: A target for management of primary osteoporosis in experimental rat model
Enas A. Fouad-Elhady, Hadeer A. Aglan, Rasha E. Hassan, Hanaa H. Ahmed, Gilane M. Sabry
Heliyon.2020; 6(2): e03341. CrossRef - Aromatase inhibitors attenuate the effect of alendronate in women with breast cancer
Sung Hye Kong, Jung Hee Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism.2020; 38(5): 730. CrossRef - Global estrogen receptor-α knockout has differential effects on cortical and cancellous bone in aged male mice
Rebecca K. Dirkes, Nathan C. Winn, Thomas J. Jurrissen, Dennis B. Lubahn, Victoria J. Vieira-Potter, Jaume Padilla, Pamela S. Hinton, Vance L. Trudeau
FACETS.2020; 5(1): 328. CrossRef - The Emerging Role of Osteocytes in Cancer in Bone
Emily G Atkinson, Jesús Delgado‐Calle
JBMR Plus.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of denosumab on low bone mineral density in postmenopausal Japanese women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitors for non-metastatic breast cancer: 24-month results
Katsuhiko Nakatsukasa, Hiroshi Koyama, Yoshimi Ouchi, Hisako Ono, Kouichi Sakaguchi, Takayuki Matsuda, Makoto Kato, Takashi Ishikawa, Kimito Yamada, Mana Yoshimura, Kei Koizumi, Teruhisa Sakurai, Hideo Shigematsu, Shunji Takahashi, Shinichiro Taira, Masat
Breast Cancer.2019; 26(1): 106. CrossRef - Association of Wnt Inhibitors, Bone Mineral Density and Lifestyle Parameters in Women with Breast Cancer Treated with Anastrozole Therapy
Kristina Bojanić, Ines Bilić Ćurčić, Lucija Kuna, Tomislav Kizivat, Robert Smolic, Nikola Raguž Lučić, Kristina Kralik, Vatroslav Šerić, Gordana Ivanac, Sandra Tucak-Zorić, Aleksandar Včev, Martina Smolić
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2018; 7(9): 287. CrossRef - Management of Aromatase Inhibitor-Associated Bone Loss (AIBL) in postmenopausal women with hormone sensitive breast cancer: Joint position statement of the IOF, CABS, ECTS, IEG, ESCEO, IMS, and SIOG
Peyman Hadji, Matti S. Aapro, Jean-Jacques Body, Michael Gnant, Maria Luisa Brandi, Jean Yves Reginster, M. Carola Zillikens, Claus-C. Glüer, Tobie de Villiers, Rod Baber, G. David Roodman, Cyrus Cooper, Bente Langdahl, Santiago Palacios, John Kanis, Nass
Journal of Bone Oncology.2017; 7: 1. CrossRef - Effects of raloxifene against letrozole-induced bone loss in chemically-induced model of menopause in mice
Abul Kalam, Sushama Talegaonkar, Divya Vohora
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2017; 440: 34. CrossRef - Sclerostin: an Emerging Target for the Treatment of Cancer-Induced Bone Disease
Michelle M. McDonald, Jesus Delgado-Calle
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2017; 15(6): 532. CrossRef - Differential profile of letrozole and exemestane on bone turnover markers in vinylcyclohexene diepoxide treated ovotoxic female mice
Abul Kalam, Sushama Talegaonkar, Divya Vohora
Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology.2016; 30(5): 429. CrossRef - Osteoblasts Are the Centerpiece of the Metastatic Bone Microenvironment
Hyo Min Jeong, Sun Wook Cho, Serk In Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 485. CrossRef
- Voluntary Wheel Running Partially Compensates for the Effects of Global Estrogen Receptor-α Knockout on Cortical Bone in Young Male Mice


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



